brain tumor
What Is a Tumor?
A tumor is a mass of tissue that's formed by an accumulation of abnormal cells. Normally, the cells in your body age, die, and are replaced by new cells. With cancer and other tumors, something disrupts this cycle. Tumor cells grow, even though the body does not need them, and unlike normal old cells, they don't die. As this process goes on, the tumor continues to grow as more and more cells are added to the mass.
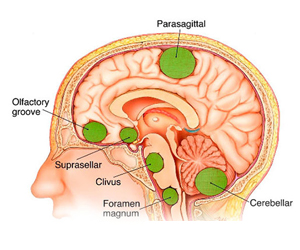
Primary brain tumors emerge from the various cells that make up the brain and central nervous system and are named for the kind of cell in which they first form. The most common types of adult brain tumors are gliomas as in astrocytic tumors. These tumors form from astrocytes and other types of glial cells, which are cells that help keep nerves healthy.
The second most common type of adult brain tumors are meningeal tumors. These form in the meninges, the thin layer of tissue that covers the brain and spinal cord.
Causes:
Brain tumors that begin in the brain
Primary brain tumors originate in the brain itself or in tissues close to it, such as in the brain-covering membranes (meninges), cranial nerves, pituitary gland or pineal gland.
Primary brain tumors begin when normal cells acquire errors (mutations) in their DNA. These mutations allow cells to grow and divide at increased rates and to continue living when healthy cells would die. The result is a mass of abnormal cells, which forms a tumor.
Primary brain tumors are much less common than are secondary brain tumors, in which cancer begins elsewhere and spreads to the brain.

Examples include:
Gliomas.
These tumors begin in the brain or spinal cord and include astrocytomas, ependymoma, glioblastomas, oligoastrocytomas, and oligodendrogliomas.Meningiomas.
A meningioma is a tumor that arises from the membranes that surround your brain and spinal cord (meninges). Most meningiomas are noncancerous.Acoustic neuromas (schwannomas).
These are benign tumors that develop on the nerves that control balance and hearing leading from your inner ear to your brain.Pituitary adenomas.
These are mostly benign tumors that develop in the pituitary gland at the base of the brain. These tumors can affect the pituitary hormones with effects throughout the body.Medulloblastomas.
These are the most common cancerous brain tumors in children. A medulloblastoma starts in the lower back part of the brain and tends to spread through the spinal fluid. These tumors are less common in adults, but they do occur.PNETs.
Primitive neuroectodermal tumors (PNETs) are rare, cancerous tumors that start in embryonic (fetal) cells in the brain. They can occur anywhere in the brain.Germ cell tumors.
Germ cell tumors may develop during childhood where the testicles or ovaries will form. But sometimes germ cell tumors move to other parts of the body, such as the brain.Craniopharyngiomas.
These rare, noncancerous tumors start near the brain’s pituitary gland, which secretes hormones that control many body functions. As the craniopharyngioma slowly grows, it can affect the pituitary gland and other structures near the brain.
